Vacuums seem simple: you pump out the air until you reach the desired low pressure. However, for a high vacuum, simply pumping out the air is not enough. To achieve this, you must take extreme measures. For many engineers though, this topic doesn’t always come naturally. High Tech Institute teaches them the tricks of the trade.
More and more, processes in the high-tech industry require a highly controlled environment. Consider the electron microscopes from Thermo Fisher or the EUV systems from ASML. If you insert air into their systems, electron beams are scattered and the EUV light gets absorbed. Therefore, a high vacuum is an absolute necessity. Contamination is also a product killer in the production of displays. Any amount of moisture in the air would prove to be disastrous for OLED materials and the display would be a total loss.
The bar is getting higher and higher. “As long as I can remember, the pressure in electron microscopes should not exceed 10-10 mbar,” says Mark Meuwese, vacuum specialist at Settels Savenije Van Amelsvoort. “But the requirements are also becoming stricter in other applications. For example, soft x-ray systems used to be able to deal with 10-3 mbar. Nowadays, 10-7 is the new standard. With increasing accuracies, come more sensitive sensors that are more susceptible to pollution or disturbance by the atmosphere present.”
 Mark Meuwese is involved in the 4-day training ‘Basics and design principles for ultra-clean vacuum‘.
Mark Meuwese is involved in the 4-day training ‘Basics and design principles for ultra-clean vacuum‘.
“The fuller you build your vacuum system, the greater the chance of contamination,” says Mark Meuwese of Settels Savenije Van Amelsvoort. Up to 10-8 mbar, it’s all relatively simple, Meuwese knows. “Of course, you still have to work hard, but if you want to go even further, the challenges increase exponentially, and the system will be many times more expensive. A water molecule is a dipole and therefore sticks to surfaces. You can pump it off better if you put enough energy into it. The easiest method for this is to heat the vacuum chamber. But by creating a temperature distribution, you introduce the risk that the evaporated elements will settle on cold surfaces, in the worst case on the sensor, the samples or the product. Moreover, many sensor systems cannot withstand high temperatures. 10-8 mbar is the limit at which everything goes well.”
Meuwese does not expect that the bulk of the applications will require lower pressures in the foreseeable future. The requirements can get stricter for specialized research work. “The limit is at 10-12 – 10-13, I estimate. And for that, you can hardly build a machine. Everything you introduce into the vacuum chamber is too much. The vessel and the pressure sensor are already too polluting, and even the most advanced pump leaks too much back into the system.”
Fingerprint
At its base, vacuum technology is simple. It starts with a vessel to which you connect a pump. You continue to pump air out until the pressure reaches the desired level. In practice, such a system is of little use. After all, you want to carry out processes in that vacuum. So, everything has to be in the vessel. In fact: you often want the space you are working in to be full of mechanics, sensors and other components. How can you build a vacuum chamber and still achieve a good vacuum level? This is one of the things you learn at an intensive training like “Basics & design principles for ultra-clean vacuum” of High Tech Institute.
“The more components you put in, the greater the chance of contamination,” says Meuwese, one of the teachers during the training. “The surface alone causes contamination through outgassing, and everything you place in the vessel means more surface, and therefore more outgassing. You have to pay attention to that.”
'A fingerprint lasts for weeks.'
How can you take a vacuum environment into account in your design? “There are a number of do’s and don’ts that we cover during the training. To begin with, there is, of course, a list of materials that are suitable for vacuum. Stainless steel is really good and you can also use aluminum without any problems. Brass, however, is not suitable because it contains zinc that evaporates at 300 degrees at 10-3 mbar. Many companies have a list of materials and coatings its engineers are allowed to use.”
Rust is also out of the question because it is porous and contains water that gasses out – meaning a proper brushing is the way of life. “A simple fingerprint can make you suffer for weeks. There are a surprisingly large number of molecules in a fingerprint, so it takes a long time before everything is gone. And there’s no guarantee you’ll be able to pump it out at all,” says Meuwese. Proper cleaning is a profession in its own right and is discussed extensively during training. Since fat is a no-no, ball bearings are a no-go. Designers have to rely heavily on elastic elements such as leaf springs and cross-spring hinges. “Or on ball bearings with ceramic balls, or fully ceramic bearings, since they do not need any lubricant.”
Little legs
Designers must also pay close attention to the shape and construction of the components. “For example, they should avoid sharp edges. If you polish it with a cotton swab or a cloth, remnants will get caught up in it,” Meuwese explains. “A bolt in a blind hole traps a volume of air. If you empty the barrel, it will leak out. Remember that the gas law states that pV/T is constant. If you want to reach 10-7 mbar, that small volume becomes ten orders larger. “Potholes are annoying because water remains in them after rinsing. “So blind holes are also to be avoided. And if you drill a hole to let the water out, it should not be too small. Due to the capillary action, the water will otherwise remain in the hole.’
'Fat is a no-no in a vacuum, so moving is done with elastic elements.'
If you use electrical discharge machining to create a part, there must not be any right angles in the pattern. “That is a different way of thinking. It is not about the most efficient design, but about preventing edges and corners. You have to curve everything and that is always a challenge. With some common sense and experience, you will eventually work it out.”
Even connecting two components in a vacuum is not straightforward. The surfaces are never flat enough to make them fit perfectly. A gap always remains – no matter how small – where air or contaminants are trapped. For the vacuum pump it is more convenient if you separate the two parts with little legs. Half a millimeter will often suffice.
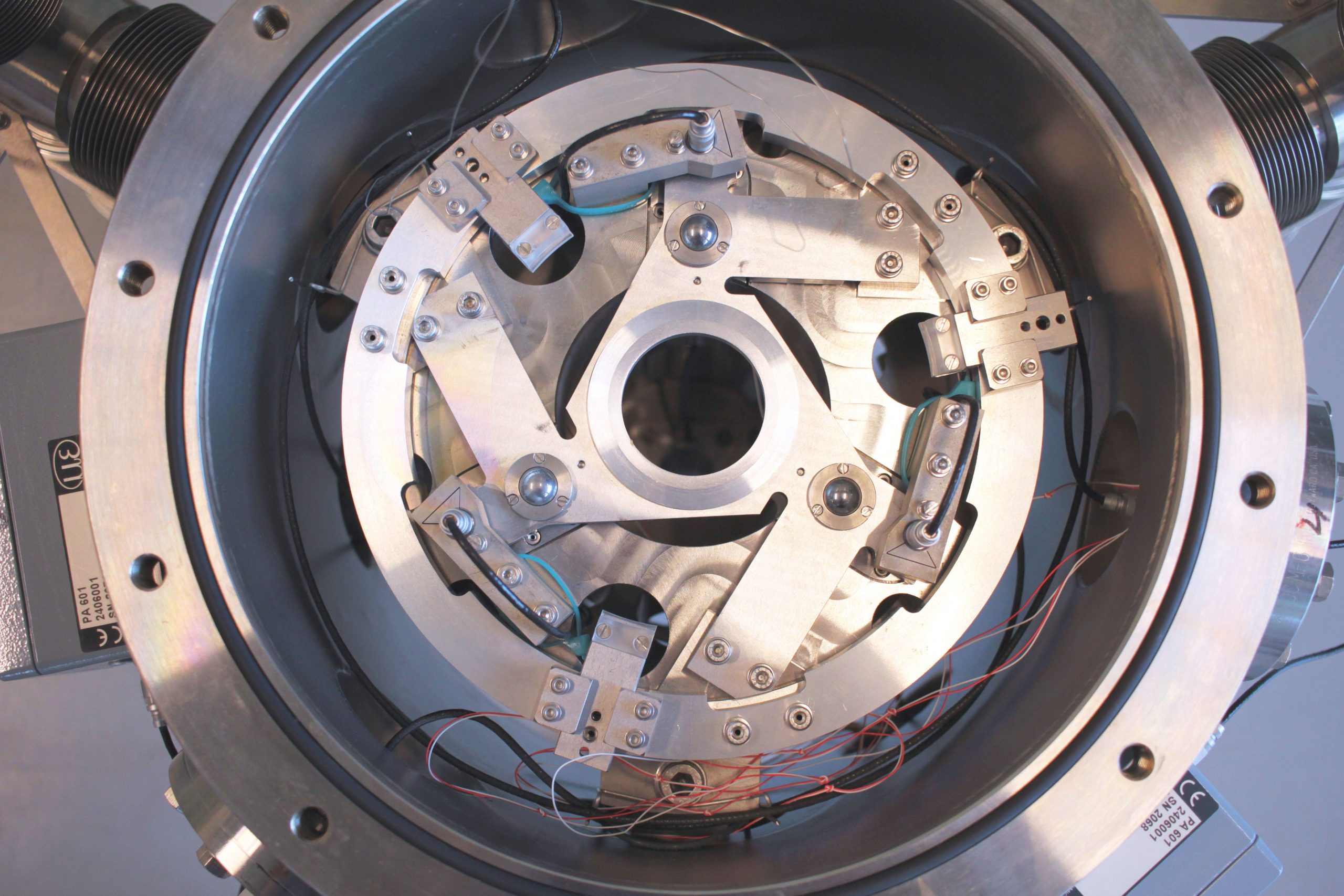 Fat is a no-no in a vacuum, so moving is done with elastic elements.
Fat is a no-no in a vacuum, so moving is done with elastic elements.
Cheating
The training of High Tech Institute in the past was mainly about vacuum technology. In recent years, more attention has been paid to ultraclean. “Vacuum is easier to understand; you pump until you reach the desired pressure,” says Meuwese. “For ultraclean, that is just the first step. Afterwards, you fill the barrel again with a “clean” gas, which, for example, no longer contains any water. But how can you backfill without polluting the barrel again? Nowadays, we also deal with that challenge during the course.”
'A vacuum is more thermally challenging than ultraclean.'
For a designer, there is little distinction between vacuum or ultraclean. The biggest difference is in the thermal properties. In a vacuum, heat transfer is very bad because there is no conductive medium. Which means no convection and no conduction, only radiation and you need a large temperature difference for that. “In vacuum, therefore, everything becomes hot by definition,” Meuwese knows. “Cooling can be done through closed channels with water, along and through the components. Or by making a thermal connection to a cold part of the system. There are also complex alternatives such as a helium backfill solution where you apply local low pressure with molecules that can transfer heat. Actually, that is cheating,” Meuwese says with a smile.

“A vacuum is more thermally challenging than ultraclean”, says Mark Meuwese.
Sense
The growing importance of vacuum technology and ultraclean means that more and more engineers must be aware of the matter. Meuwese observes that although the level across the board is rising, there is still much to be gained. “Most people who come from college or university have a sense of technology. They sense that a thick I-profile beam can take more weight than a thin I-beam. They have much less of a natural sense for vacuum. If I tell someone that I can evaporate 1015 molecules within a certain time and there are 1018, I am a factor of a thousand off, but they don’t know what that means. A vacuum is more abstract than mechanics. Mbar liters per second: it does not ring a bell for many engineers.”
Schools nowadays are paying more attention to the subject. Certainly, in the Eindhoven region, more and more students master the basic knowledge. “Coincidentally, I now have a student from Enschede, and it is less widely represented there. More on the University of Twente, but much less at higher professional education. It is also closely related to the Eindhoven region, but something like vapor deposition is used all over the world and you need vacuum knowledge for that. ”
This article is written by Alexander Pil, tech editor of High-Tech Systems.
Recommendation by former participants
By the end of the training participants are asked to fill out an evaluation form. To the question: 'Would you recommend this training to others?' they responded with a 8.3 out of 10.










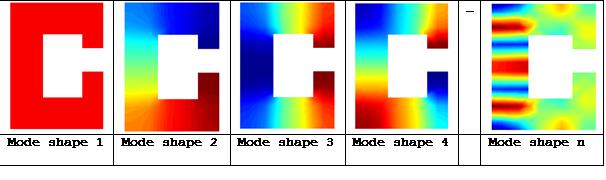





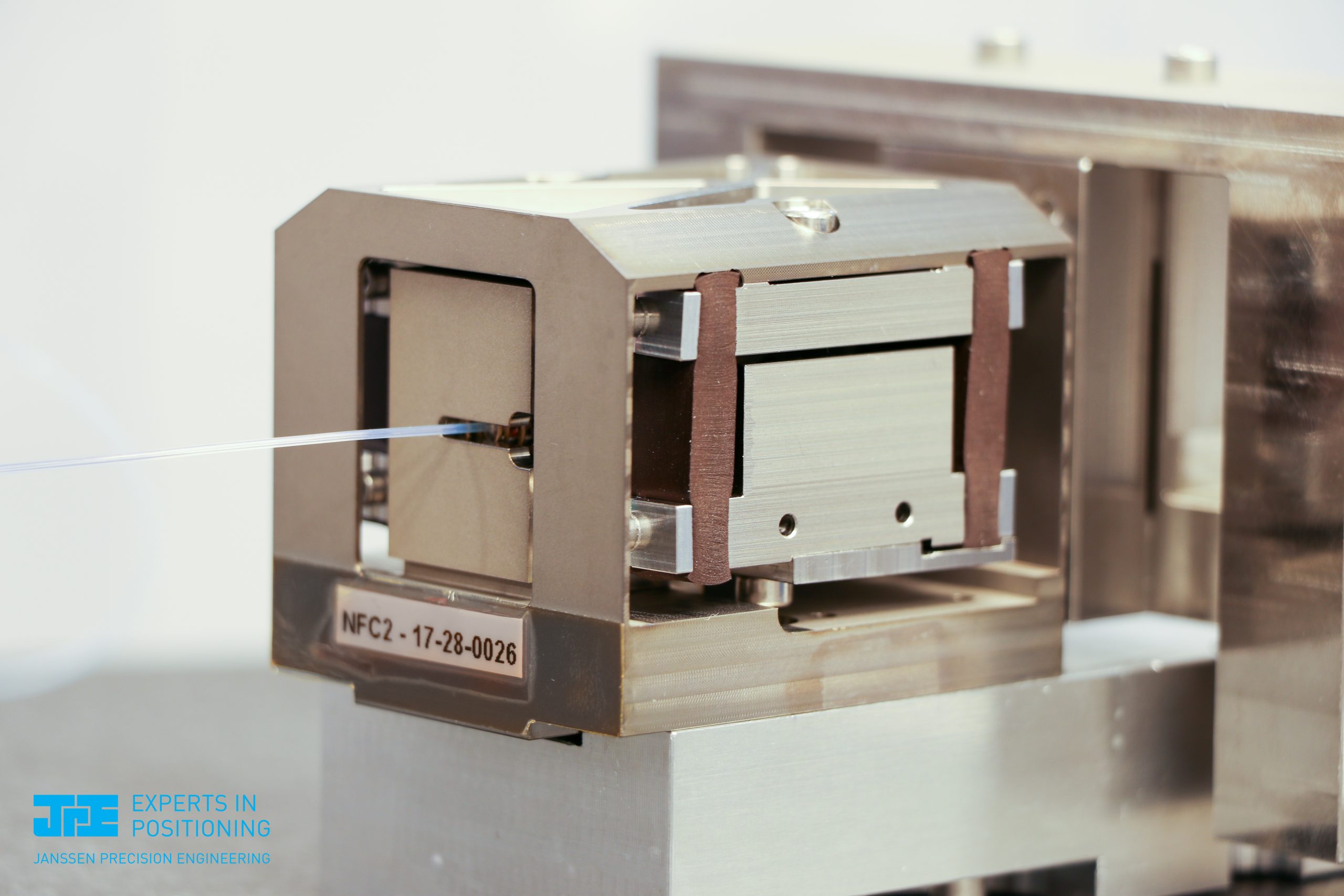
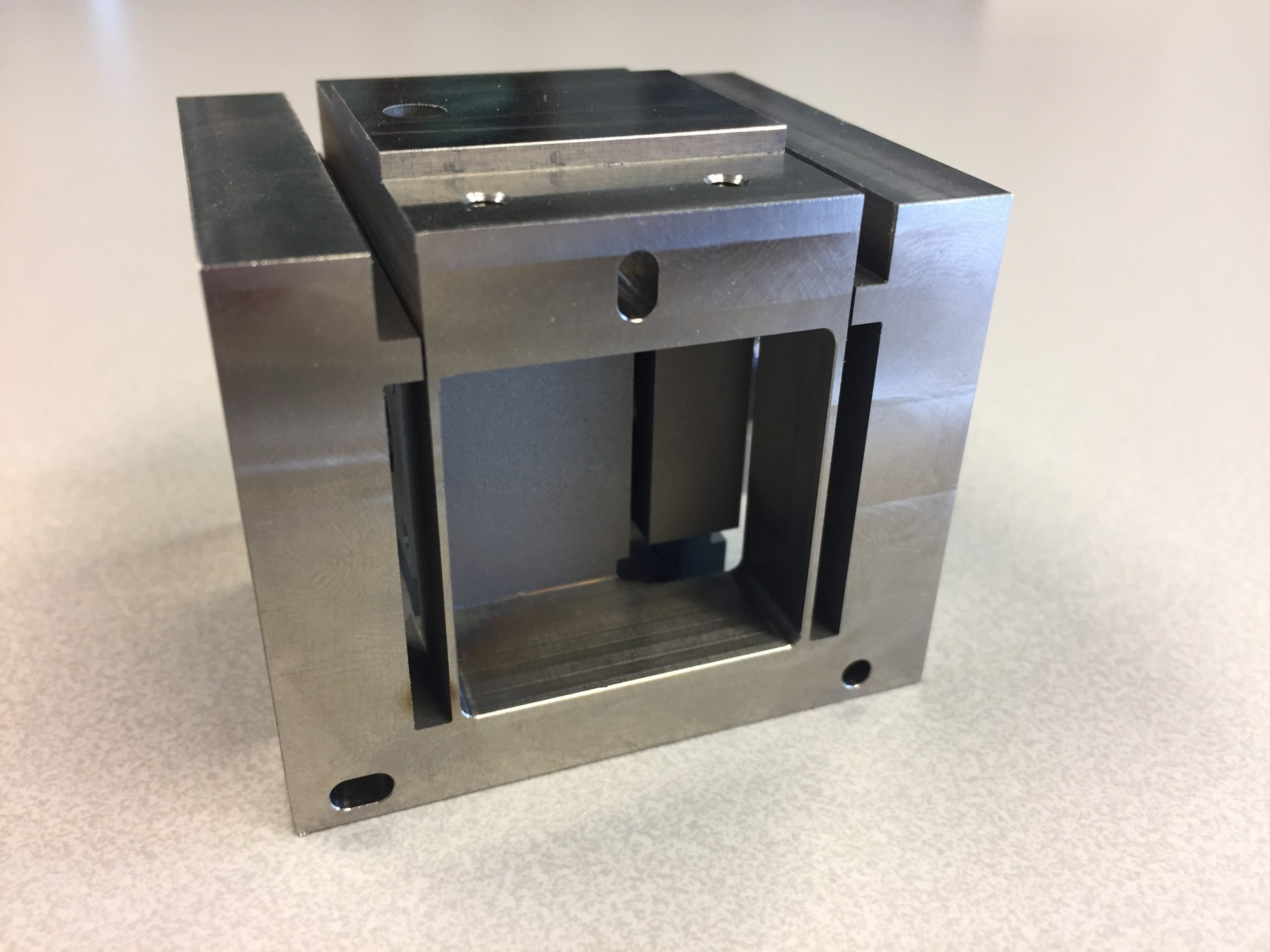
 Hans Vermeulen shows how damping can reduce a resonance peak on a graph.
Hans Vermeulen shows how damping can reduce a resonance peak on a graph.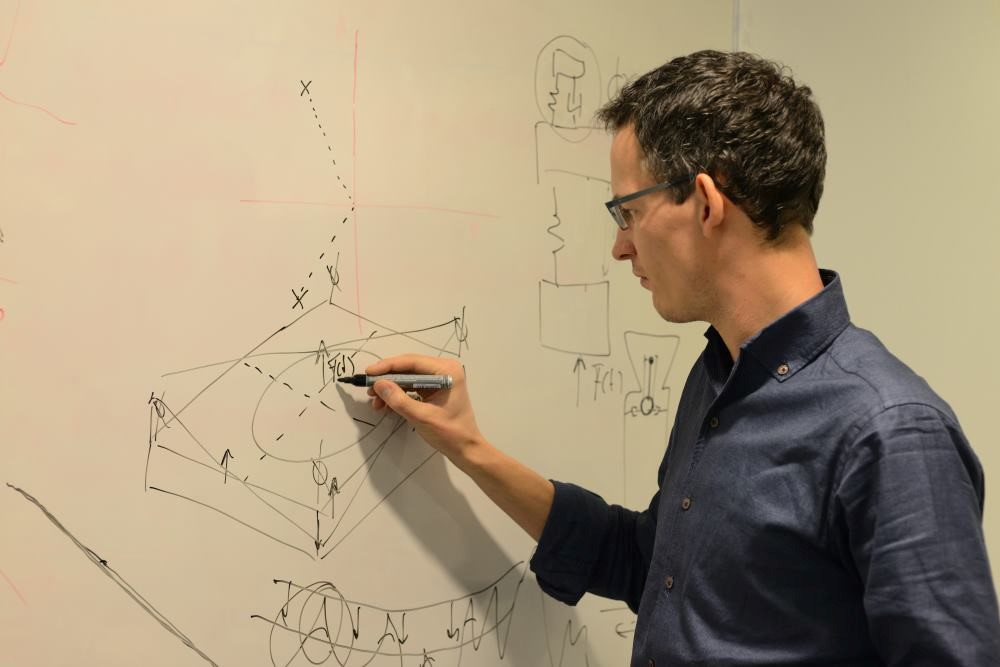












 Huub Janssen is the new figurehead of the Design Principles training course. Like Piet van Rens, he comes from the school of thought of Professor Wim van der Hoek. The precision engineer honoured his mentor by naming the new meeting and demo room at Janssen Precision Engineering after the person who had inspired him, Wim van der Hoek.
Huub Janssen is the new figurehead of the Design Principles training course. Like Piet van Rens, he comes from the school of thought of Professor Wim van der Hoek. The precision engineer honoured his mentor by naming the new meeting and demo room at Janssen Precision Engineering after the person who had inspired him, Wim van der Hoek.

